Main Formulas you have to memorize to pass PMP Exam - Version 6
Below are the main formulas that shall be memorized for PMP - Ver. 6 Exam:
1. Standard Deviation (SD)
SD is a way to measure how much is the variation from the mean.
usually it is used to analyze data. Standard Deviation is represented by using the symbol sigma (σ).
Sigma is the difference of distribution values on any end and in middle.
σ = (Pessimistic – Optimistic) / 6
A low value of SD shows that the data points are close to mean or average and a high value of SD shows that data points are spread over a large range.
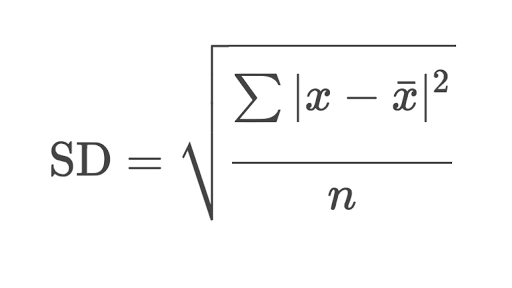
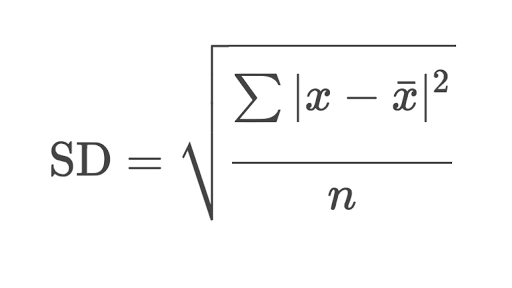
2. Earned Value
specific technique in which the actual values of the work related performance is calculated for any and all particular work components and of schedule activities
Earned Value = % complete × Budget at Completion (BAC)
For example, if the project team has completed 100 man-hours of work and project required 500 man-hours of work to complete the project, then
% Complete = 100/500 × 100 = 20%
Budget at Completion = Total budget assigned for the project (let it be $50,000 in this case)
Then, EV = 20 × $50,000 = $10,000
3. Schedule Variance (SV)
It is the difference between the earned value and the planned value.
Schedule Variance = Earned Value (EV) – Planned value (PV)
For example, if EV for an app development project is $40,000 and PV is $50,000 then
Schedule Variance = $40,000 – $50,000 = – $10,000 (which shows that project is running behind the schedule by $10,000 schedule variance)
** Negative value of SV shows that the project is behind the Schedule
** Positive value of SV shows that the project is ahead of the Schedule.
** Zero SV means that the project is exactly at the Schedule.
4. Schedule Performance Index (SPI)
It is a ratio of the earned value to the planned value.
SPI = Earned Value (EV) / Planned Value (PV)
As the same of CPI, it is also a ratio then it can have three values (=1, >1 or <1)
If SPI = 1, it indicates that project is going at the same rate as expected.
If SPI > 1, it indicates that project is going at a faster rate.
If SPI < 1, it indicates that project is going at a slower rate.
5. Cost Variance (CV)
It is the difference between earned value and actual cost.
Cost Variance (CV) = Earned Value (EV) – Actual Cost (AC)
For example, If Earned Value (EV) and Actual Cost (AC) for a project are $75,000 and $60,000 respectively then
Cost Variance = $75,000 – $60,000 = $15,000
The positive of Cost Variance shows the condition of under budget whereas the negative value of Cost Variance denotes the over budget.
The value of zero for the cost variance shows that the project is exactly at the budget.
6. Cost Performance Index (CPI)
It is the ratio of earned value to the actual cost.
CPI = EV / AC
CPI can have three values (=1, >1or <1)
If CPI = 1, then it means that the project is getting $1 for every $1 spent.
If CPI > 1, then it means that he project is getting more than $1 for every $1 spent.
If CPI < 1, then it means that he project is getting less than $1 for every $1 spent.
7. Estimate at Completion (EAC)
It is a forecasting technique to predict the future project performance.
There are four Equations to calculate EAC.
1st Equation of EAC
Estimate at Completion (EAC) = BAC / CPI
If CPI = 1 then EAC = BAC which means that the project manager are able to complete the project within the provided budget and without any forecasting analysis. Even at the starting of the project, estimate at Completion is same as that of the Budget at Completion.
2nd Equation of EAC
When the project cost estimation was flawed and the project manager wants to find the new cost estimate for the remaining works, you need to move to the activity level in order to find the cost of each activity, and then add individual costs to obtain the total cost value of the remaining works. In this case, the following formula is used to calculate the EAC
Estimate at Completion (EAC) = AC + Bottom-up ETC
3rd Equation of EAC
If a deviation happened from the estimated budget but now the project manager can perform the remaining task as per plan. This may happen because of an unexpected condition or increased in cost. so, to calculate the value of EAC in this formula, money spent to date is added to the budgeted cost for remaining project works.
Estimate at Completion = Money spent to date + Budgeted cost for the remaining work
Estimate at Completion (EAC) = AC + (BAC – EV)
4th Equation for the EAC
In this equation, both the schedule and cost are required to be taken into consideration, this formula is applied to find the value of EAC. It is given as:
Estimate at Completion (EAC) = AC + [(BAC – EV) / (CPI × SPI)]
Estimate at Completion (EAC) = AC + [(BAC – EV) / (CPI × SPI)]
Estimate at Completion = Money spent up to date + (Budgeted cost for the remaining works – Earned Value) / (Cost Performance Index × Schedule Performance Index)

8. Variance at Completion (VAC)
It is the difference of Budget at Completion and Estimate at Completion.
Variance at Completion (VAC) = BAC – EAC
Remember that a $0.0 value for VAC indicates that the project will hit the budget. A value less than $0.0 indicate that the project will be over budget and a value more than $0.0 shows that the project will be under/lower than the budget.
9. Estimate to Complete (ETC)
It is a way demonstrates which value that shall be spent on the remaining works for the project to get the project completed.
ETC = EAC – AC
10. To Complete Performance Index
It is a measurement for the cost performance that is required to be achieved with the remaining resources in order to meet a specified management target.
There are two ways to calculate the TCPI as stated below:
TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (EAC – AC)
TCPI = (BAC – EV) / (BAC – AC)
11. Communication Channels (CN)
11. Communication Channels (CN)
The number of ways by which information flows within the organization or Company.
communication channels = n (n – 1) / 2
Where ‘n’ stands for the number of stakeholders
If there are 7 stakeholders, then the number of communication channel is = 7 (7-1) / 2 = 21 channels
(Remember that a stakeholder may be an individual, a group or an organization that is affected by the decision, activity or result of the project)
** Remember that usually there is 1 direct question about this formula in PMP exam.