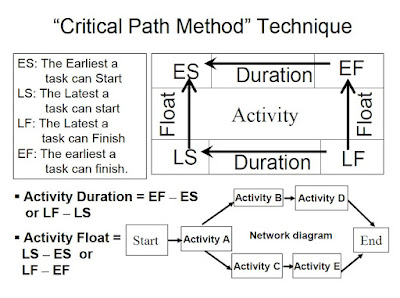
Critical Path Method (CPM)
Critical Path is the LONGEST duration path through a network diagram and determines the shortest or earliest time to complete the project.
The Critical path is calculated by Adding up the duration's of activities of each path in a network diagram. The longest path is the critical path (The longest path duration = The shortest time
a project takes to finish all its activities).
This technique calculates theoretical EARLY start & Finish dates( ES & EF ) and LATE Start & Finish ( LS & LF) dates ,for all activities Regardless for any resource limitations.
Calculations of ES,EF : performing a forward pass analysis through the schedule network [from the beginning of the project to the task and following the dependencies in the network diagram].
Calculations of LS, LF: performing a backward pass analysis through the schedule network. [from the end of the project to the task and following the dependencies in the network diagram].
Most Project Management software's calculate ES EF LS LF for you, but you must be able to calculate
them manually on PMP exam.
The resulting dates ( ES,EF,LS,LF) are not necessarily the schedule
network; rather, they indicate the followings:
- TIME PERIODS within which the schedule activities could be scheduled.
- Given activity duration
- Logical relationships.
- LEAD & LAG and other known constraints.
- Calculating ES,EF,LS,LF may be affected by the activity Total Float.
Total Float (slack): The amount of time that a schedule activity may be delayed from its early start date without delaying the project completion date or violating a schedule constraint.
Total Float is termed as schedule flexibility and is measured by the
positive difference between Early and Late dates (LF-EF or LS-ES).
- Total float may be Positive(we can wait), Negative(We need to speed up the Work on this activity) or Zero(No any delay).
- The “critical path” has either Zero or Negative total float. But critical path is normally characterized by Zero total float on the critical path.
- Adjustments to activity duration, logical relationships, leads and lags or other schedule constraints may be necessary to produce network paths with a zero or positive total float.
The activities in the critical path are called “Critical Activities” and almost always have no slack (Slack=0)
The total float provides schedule flexibility.
Once the total float for a network path has been calculated then the Free float can also be determined.
Free Float (Slack): The amount of time that an activity can be delayed without delaying the early start date of any immediate successor activity within the network path.
Project Float (Slack): The amount of time a project can be delayed without delaying the externally imposed project completion required by the customer, sponsor or management.
Near Critical Path: a Path with low float. A network diagram can have
multiple near critical paths.
Free PMP Exam
http://academyoflions.blogspot.com/2016/11/free-pmp-online-training-course.html
Float is extremely useful for:
– The project manager: Better allocation of rescourses among other areas of the project.
– Team members: To juggle multiple projects
The critical Path Method technique has the following benefits:
It proves the project time estimate.
It helps project compression.
It indicates where to focus and what to monitor.
It indicates what could be delayed.
It Shows what requires immediate action.
PM should monitor & control the Near–Critical Path as well.
Example I:
- In order to solve such questions which appear always in PMP exam, first you have to determine the possible paths exist in the chart.
(Start) - A-B-C-D-E-K - (End)
(Start) - A-B-F-G-H-J-K - (End)
(Start) - A-B-I-J-K - (End)
- Second step is to determine the length of each path based on the duration gived in the chart for each activity:
(Start) - A-B-C-D-E-K - (End) *31 Days*
(Start) - A-B-F-G-H-J-K - (End) *43 Days*
(Start) - A-B-I-J-K - (End) *33 Days*
- So based on the definition of the Critical Path which is the LONGEST duration path through a network diagram, the critical path will be the second path : (Start) - A-B-F-G-H-J-K - (End)
Example II:
The total float provides schedule flexibility.
Once the total float for a network path has been calculated then the Free float can also be determined.
Free Float (Slack): The amount of time that an activity can be delayed without delaying the early start date of any immediate successor activity within the network path.
Project Float (Slack): The amount of time a project can be delayed without delaying the externally imposed project completion required by the customer, sponsor or management.
Near Critical Path: a Path with low float. A network diagram can have
multiple near critical paths.
Free PMP Exam
http://academyoflions.blogspot.com/2016/11/free-pmp-online-training-course.html
Float is extremely useful for:
– The project manager: Better allocation of rescourses among other areas of the project.
– Team members: To juggle multiple projects
The critical Path Method technique has the following benefits:
It proves the project time estimate.
It helps project compression.
It indicates where to focus and what to monitor.
It indicates what could be delayed.
It Shows what requires immediate action.
PM should monitor & control the Near–Critical Path as well.
Example I:
- In order to solve such questions which appear always in PMP exam, first you have to determine the possible paths exist in the chart.
(Start) - A-B-C-D-E-K - (End)
(Start) - A-B-F-G-H-J-K - (End)
(Start) - A-B-I-J-K - (End)
- Second step is to determine the length of each path based on the duration gived in the chart for each activity:
(Start) - A-B-C-D-E-K - (End) *31 Days*
(Start) - A-B-F-G-H-J-K - (End) *43 Days*
(Start) - A-B-I-J-K - (End) *33 Days*
- So based on the definition of the Critical Path which is the LONGEST duration path through a network diagram, the critical path will be the second path : (Start) - A-B-F-G-H-J-K - (End)
Example II:
- First Step: draw the network diagram :
- Second Step: determine the Critical path:
- Third Step: determine the ES, EF, LS & LF for each activity:
- Now it is easily to calculate the float for each activity as the ES, EF and LS, LF are known for all activities.













ليست هناك تعليقات:
إرسال تعليق